About
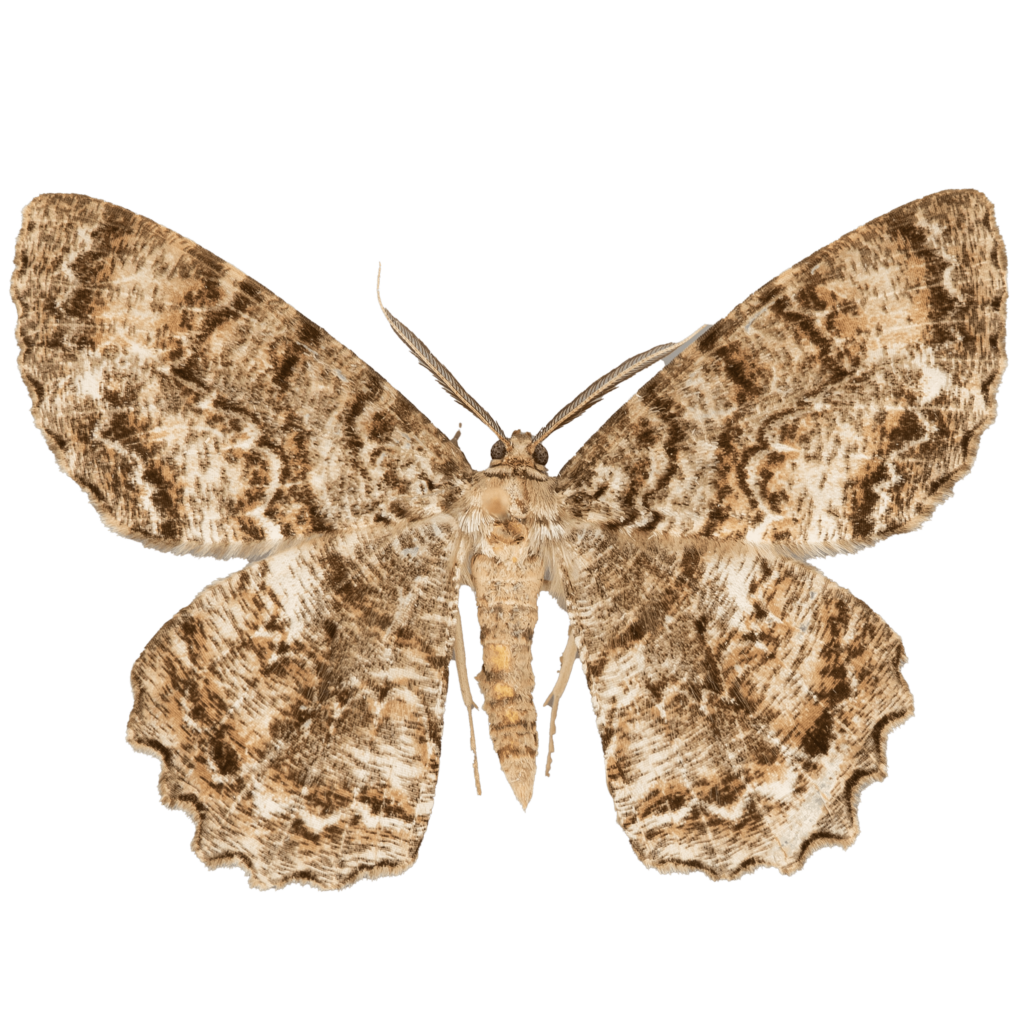
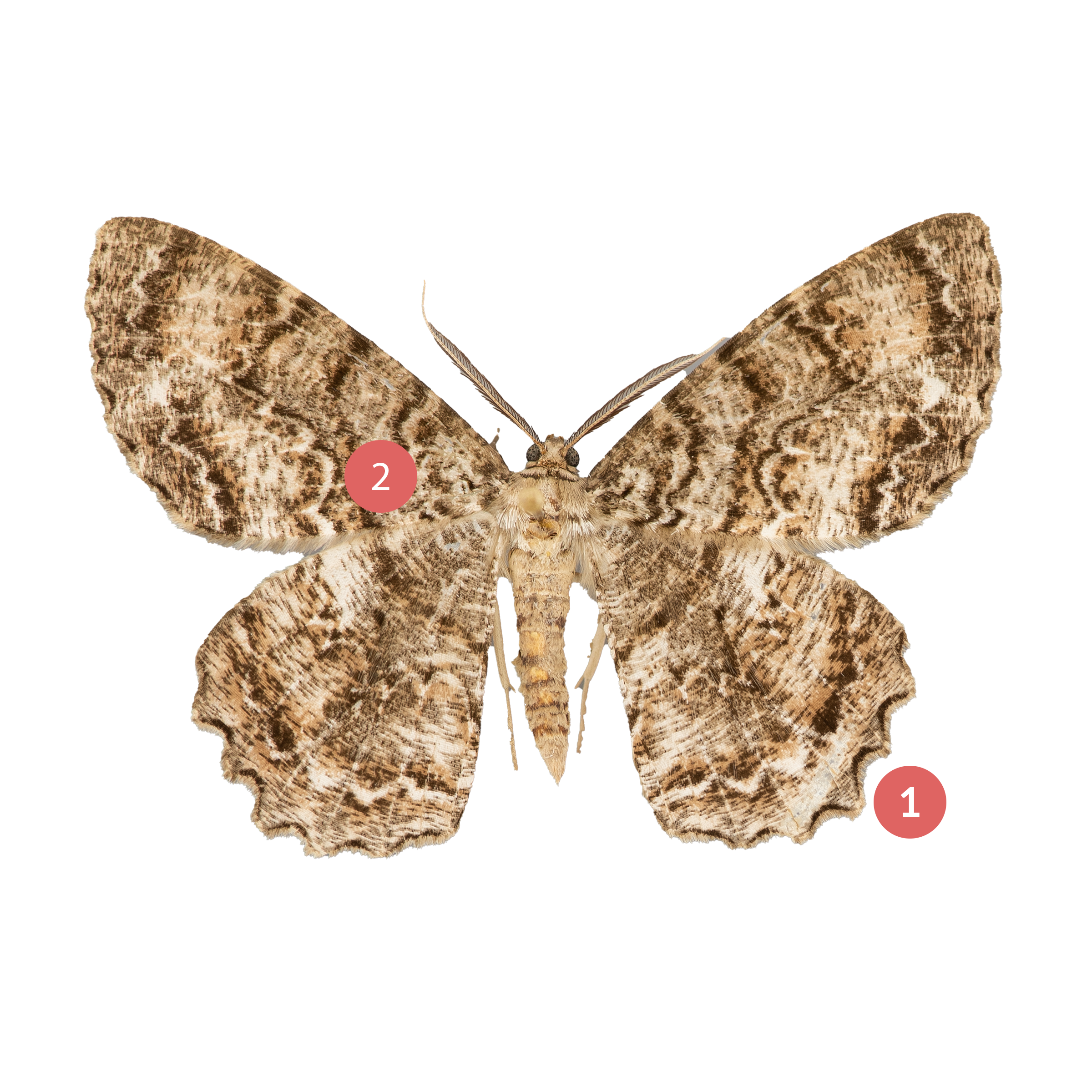
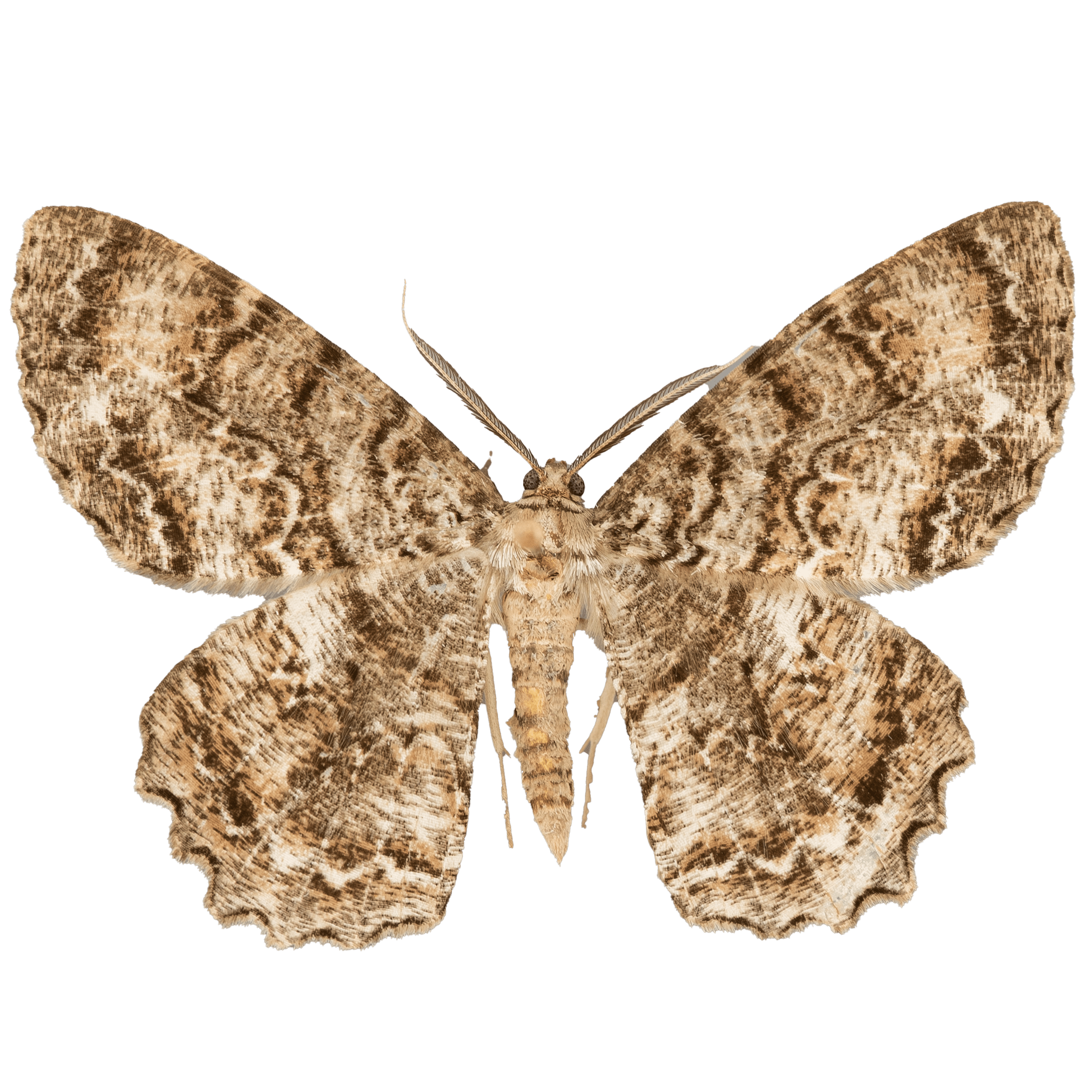
Epimecis hortaria, commonly known as the Tulip-Tree Beauty Moth, is a species of moth found in the eastern United States. One interesting characteristic of this species is that it exhibits both light and dark morphs. The light morph has a pale greenish-gray coloration, while the dark morph is characterized by a rich brown coloration with a subtle green tint.
The wingspan of the Tulip-Tree Beauty Moth ranges from 2.5 to 3.5 inches, and its wings are marked with striking silver and bronze patches. The silver patches form a distinct “Y” shape, while the bronze patches form a crescent shape along the outer edge of the wings. The moth’s forewings are long and narrow, while its hindwings are broader and have a scalloped edge.
One fun fact about the Tulip-Tree Beauty Moth is that it is named after the tulip tree, which is a preferred host plant for its caterpillars. The species is also known to use other plants, such as magnolias and sweetgums, as host plants.
forests, woodlots, urban areas, suburban areas