About
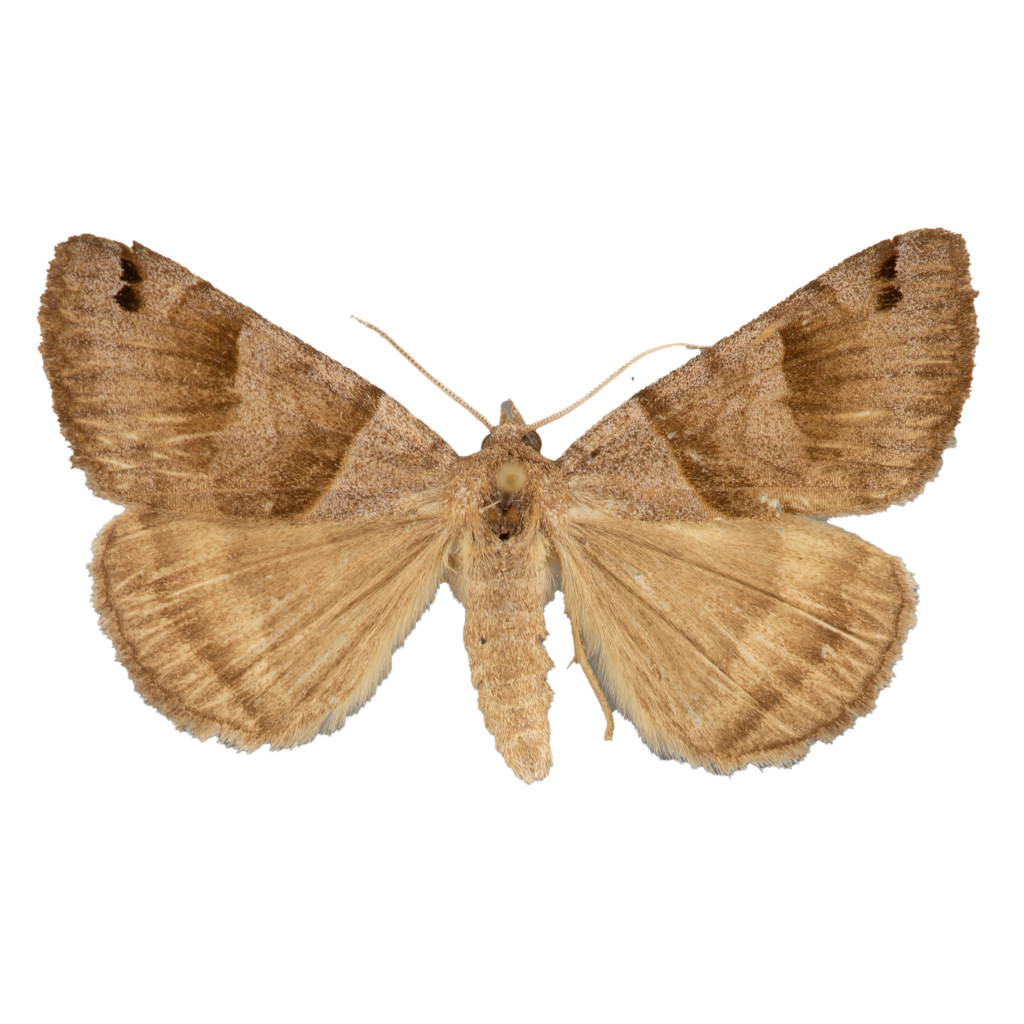
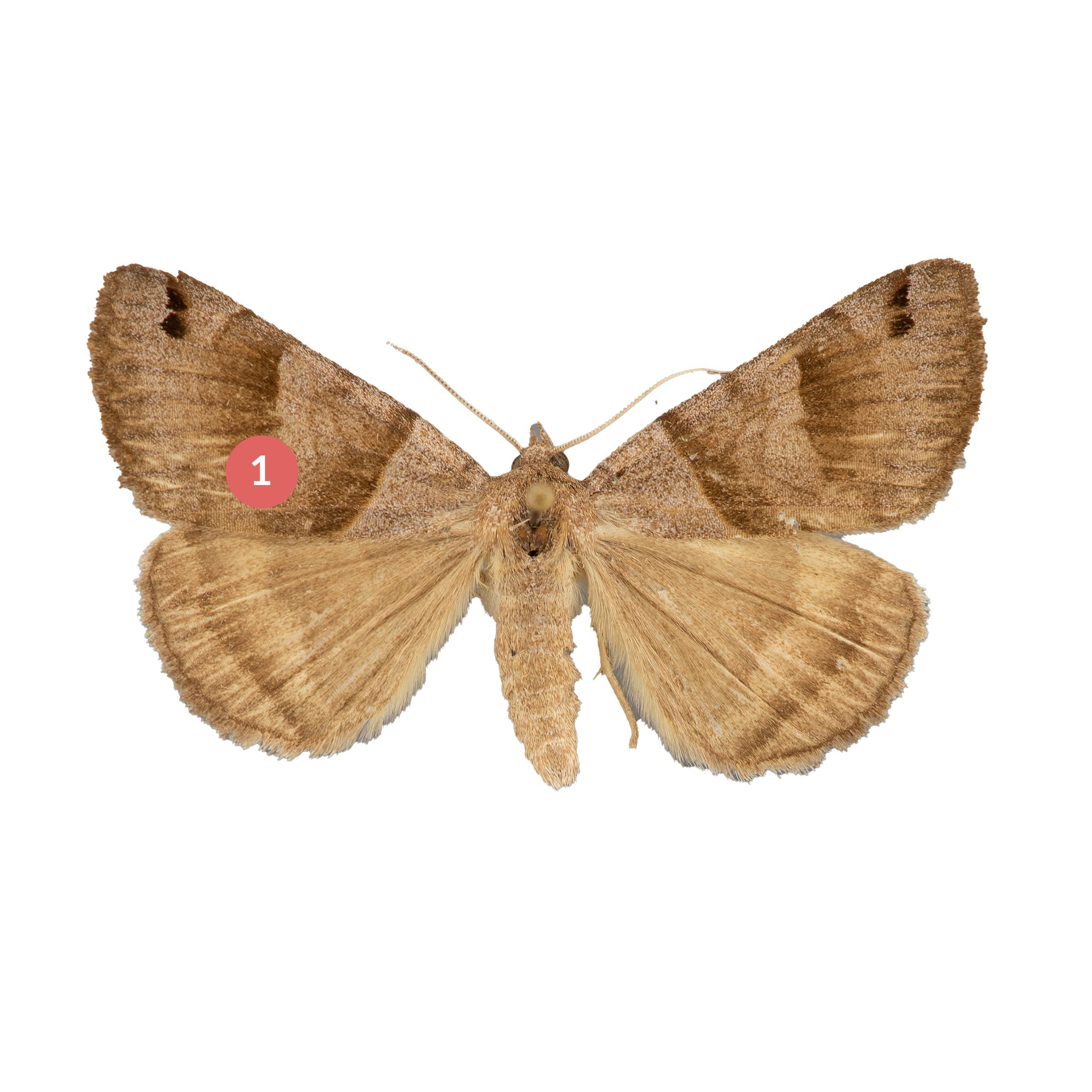
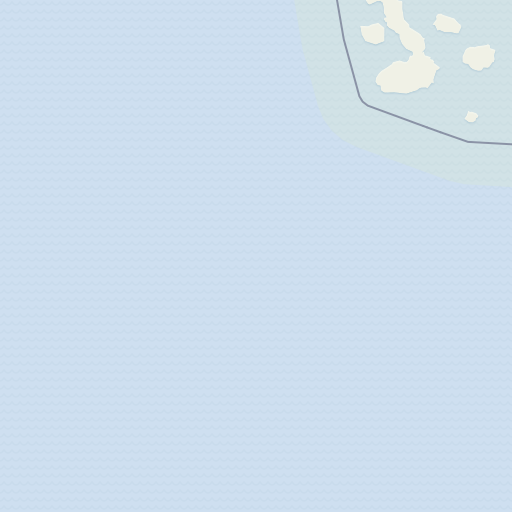
The Clover Looper (Caenurgina crassiuscula) is a moth commonly found in waste places and agricultural fields throughout North America. It is named for its distinctive looping motion, as well as its preferred habitat in clover fields. The moth has a wingspan of approximately 1 inch and is characterized by two dark arcs on each wing that resemble the letter ‘C’ when viewed from above. Its wings are typically brown or gray, with a mottled appearance that helps it blend in with its surroundings.
A fun fact about the Clover Looper is that it belongs to a family of moths known for their distinctive caterpillar behavior. Like other loopers, the Clover Looper caterpillar has only two to three pairs of prolegs, which results in its unique crawling motion. When threatened, the caterpillar will drop from its perch and dangle from a silk thread, using its looping motion to descend slowly to the ground.
fields, roadsides, waste places